5.5 All about Nitrogen in Corn
Nitrogen is necessary in the production of protein and chlorophyll of vegetation, and its deficiency causes a decrease in the amount of chlorophyll, and as a result, it leads to a decrease in photosynthesis.
It is possible to estimate the amount of nitrogen by remotely sensed data.
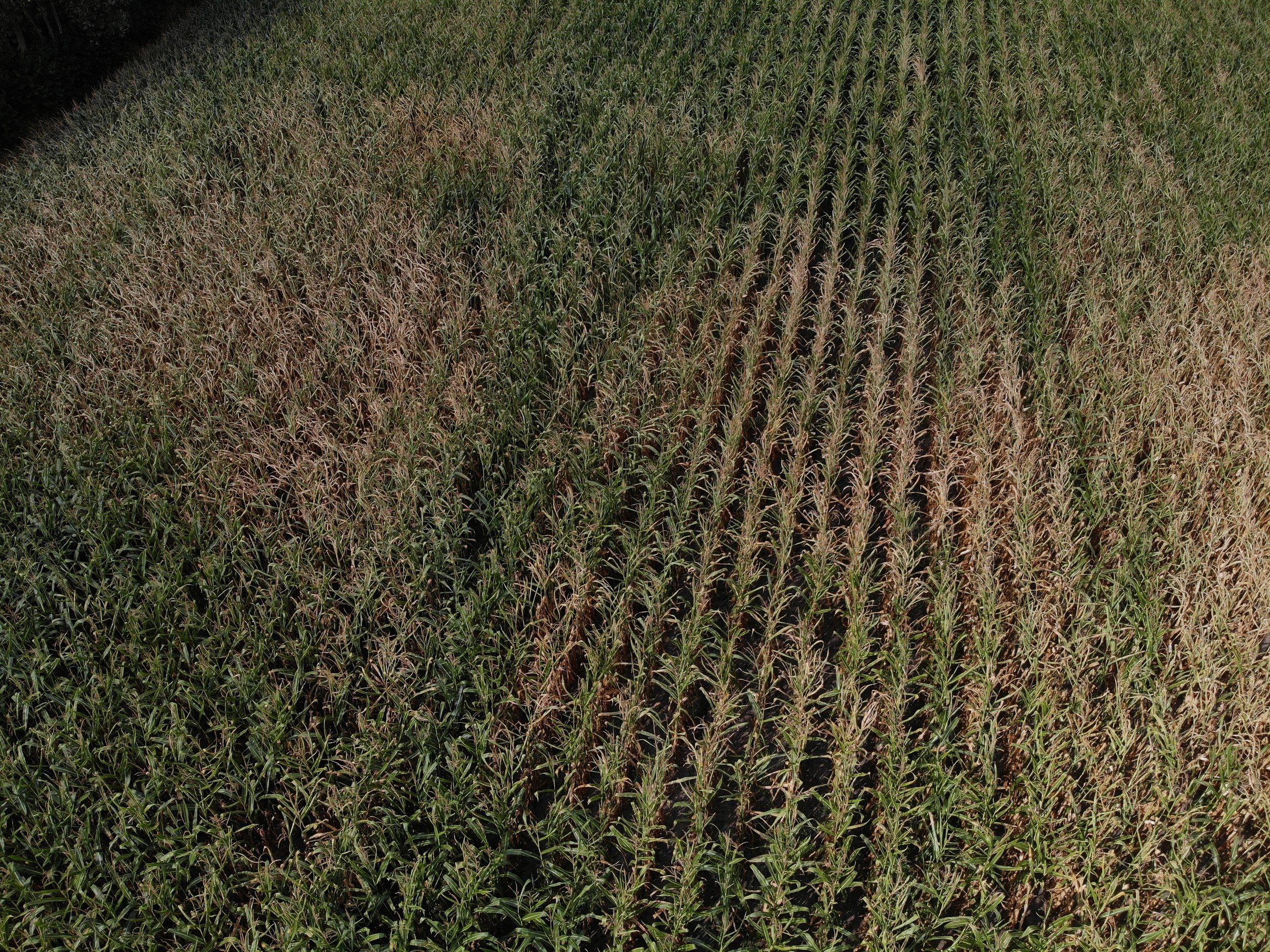
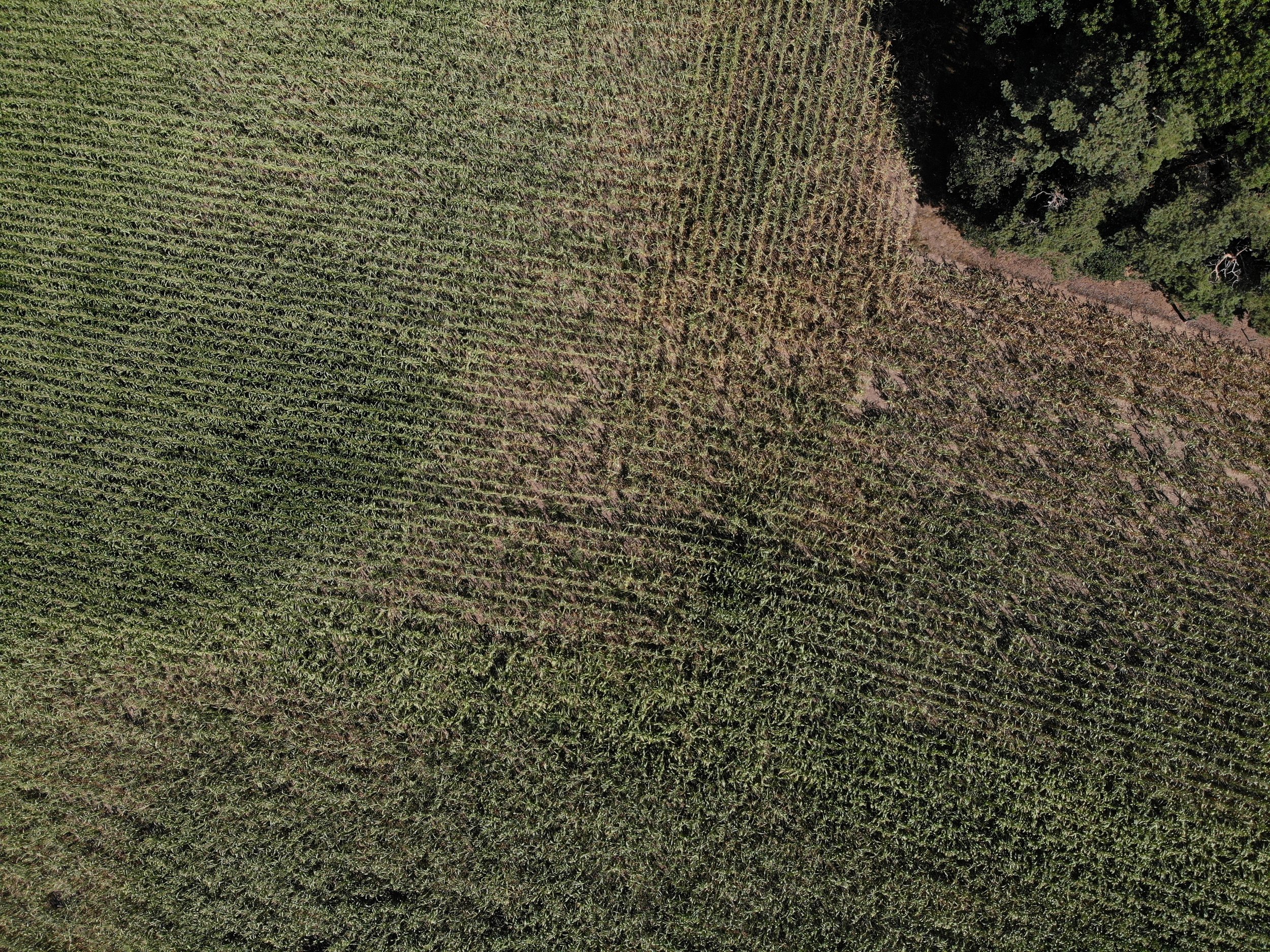
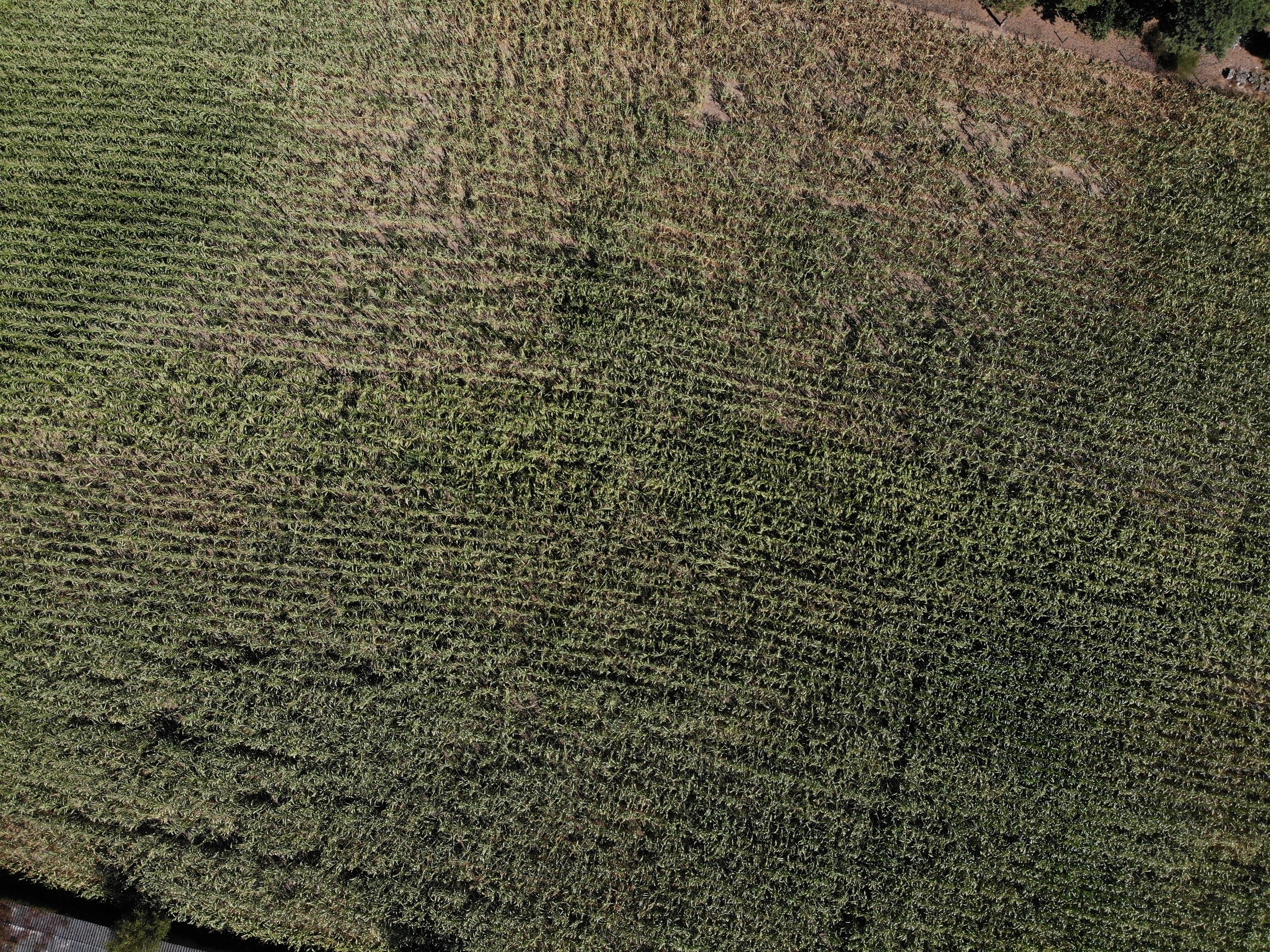
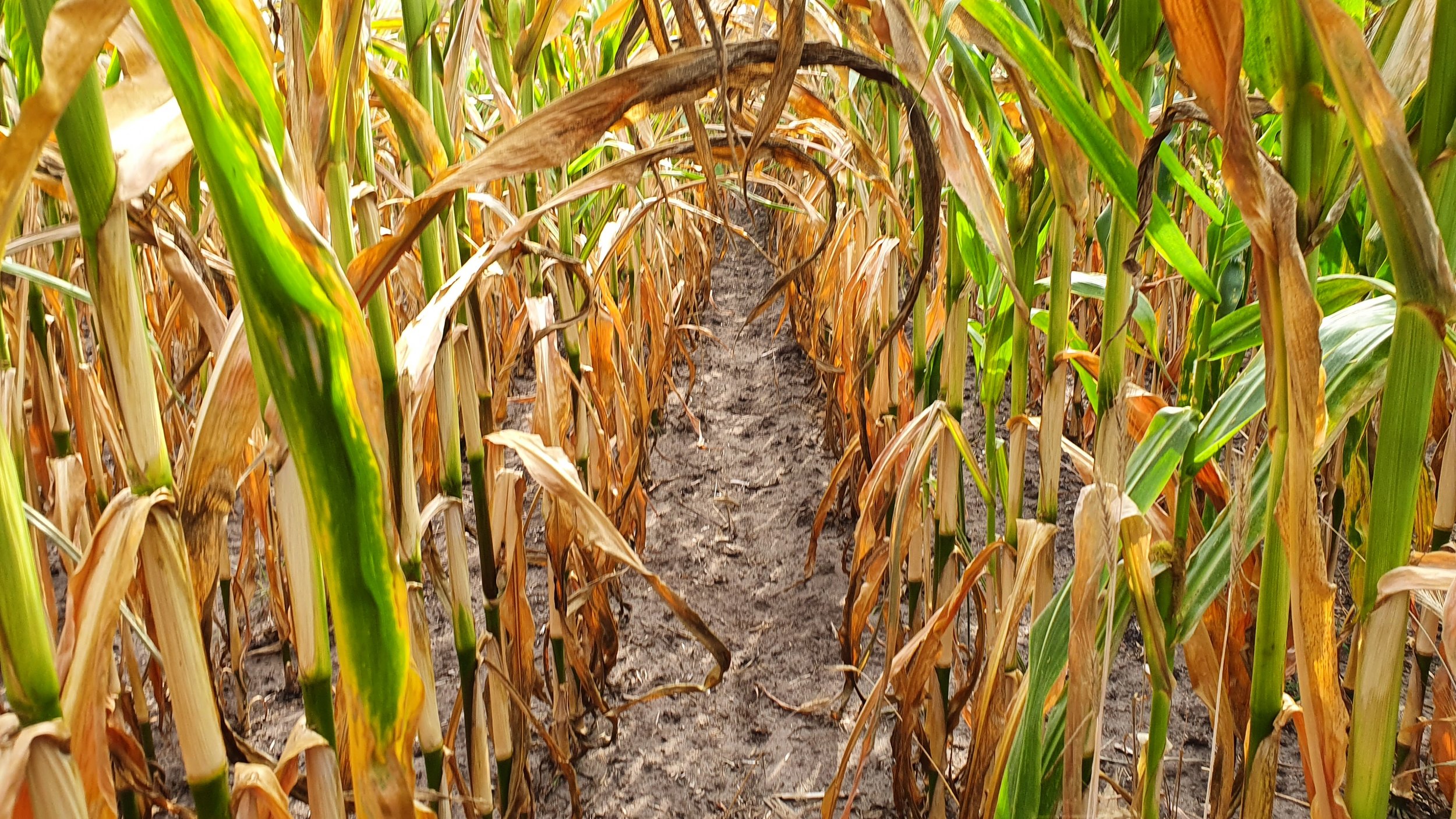
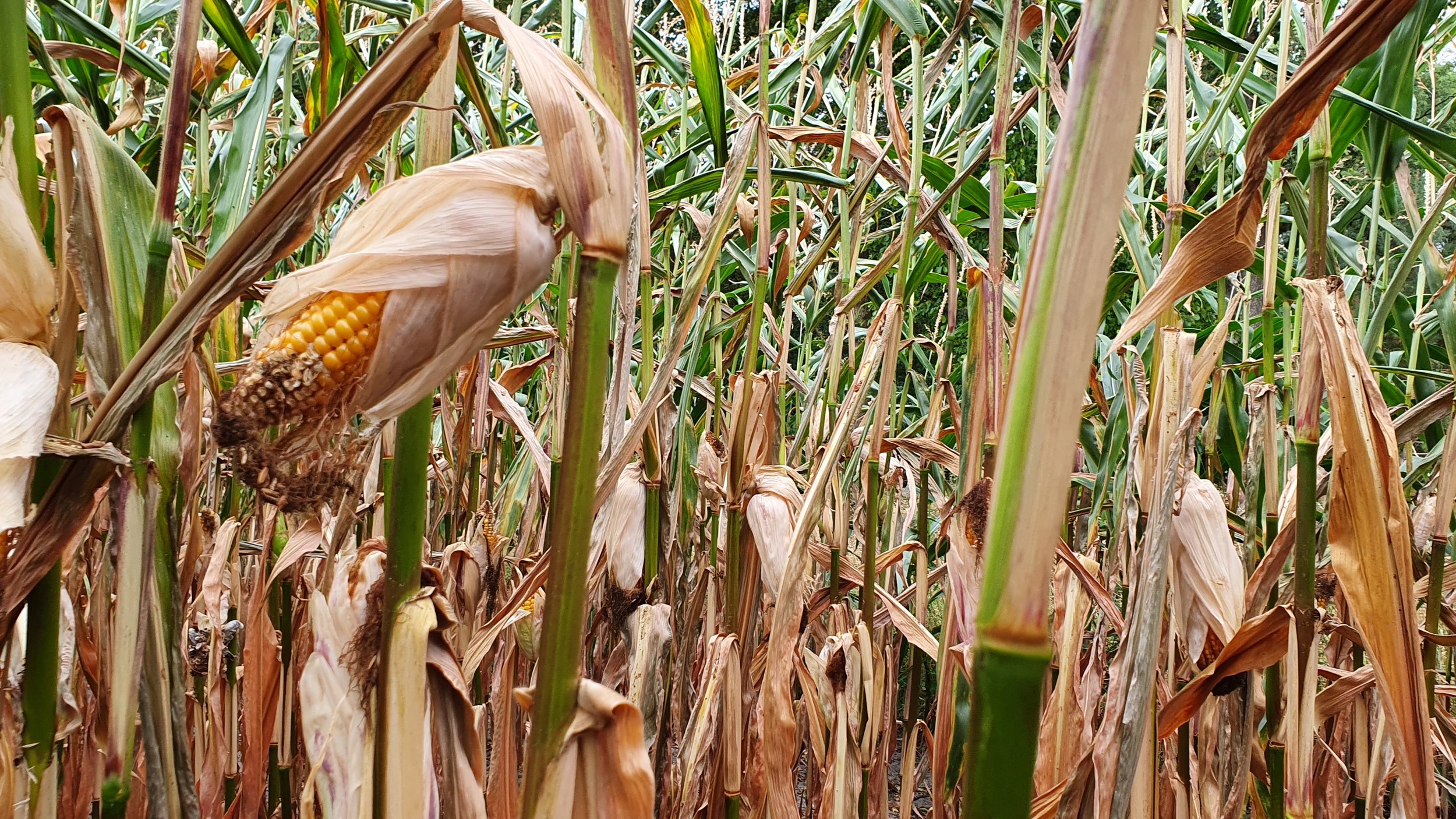
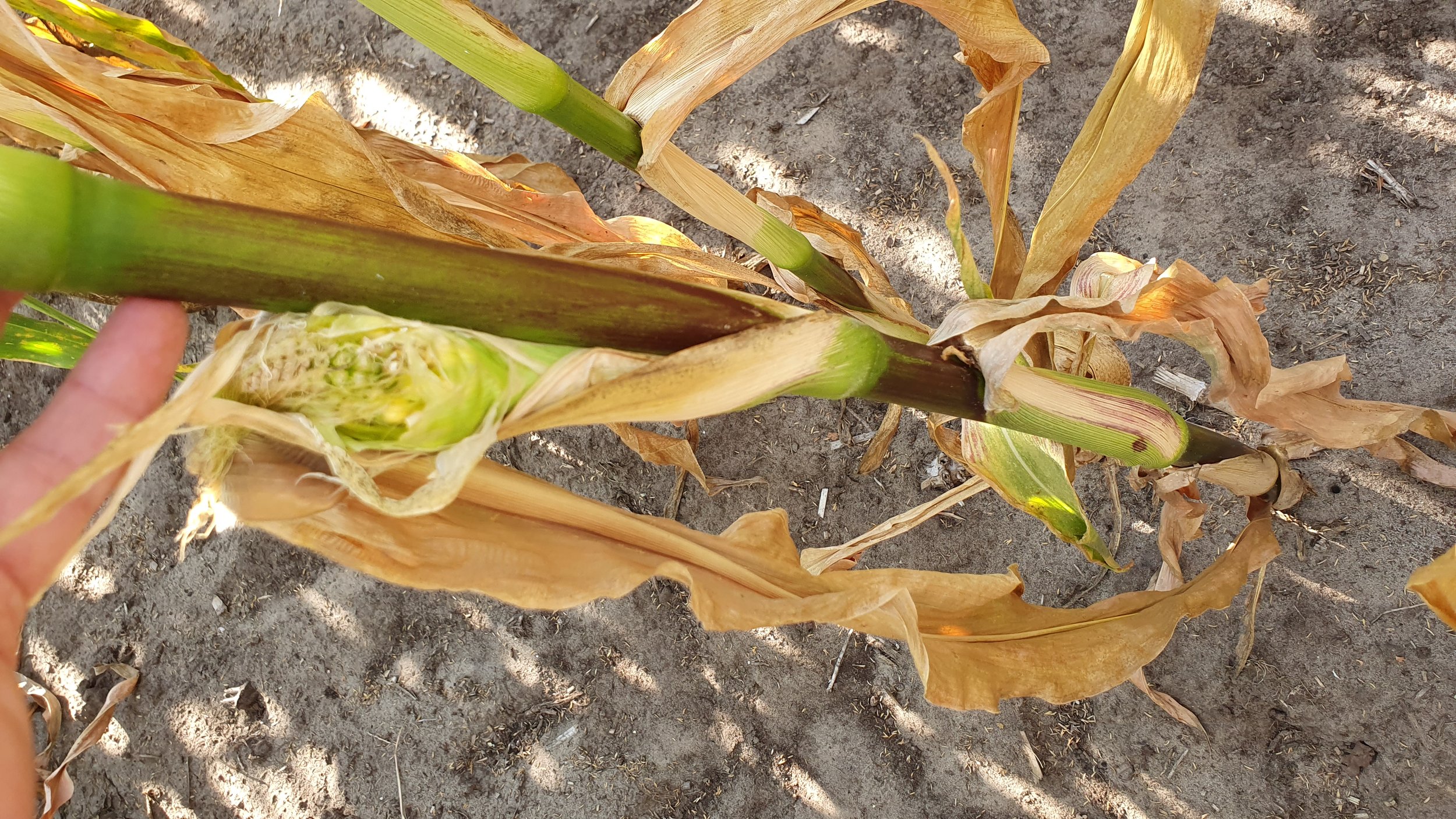
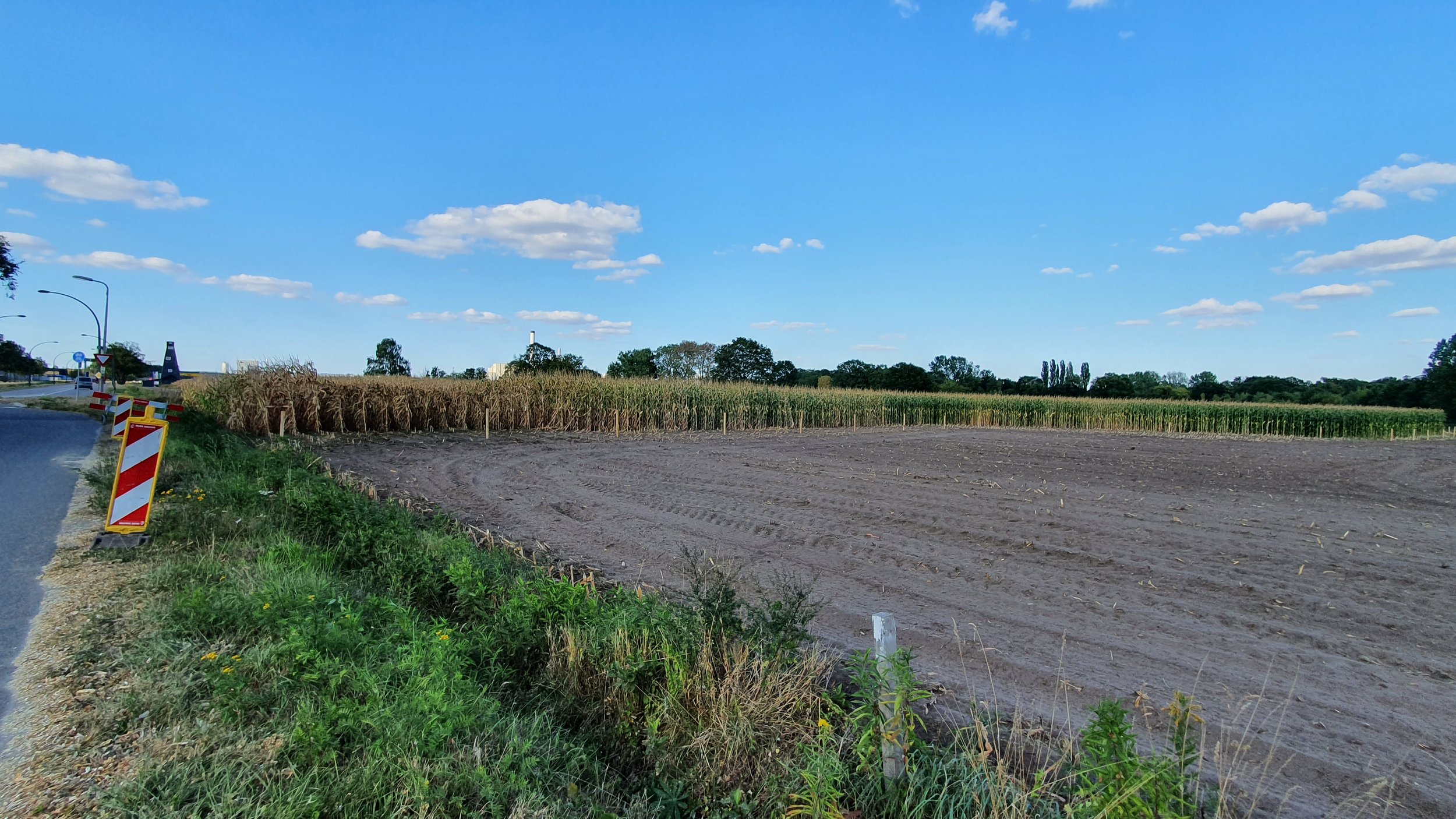
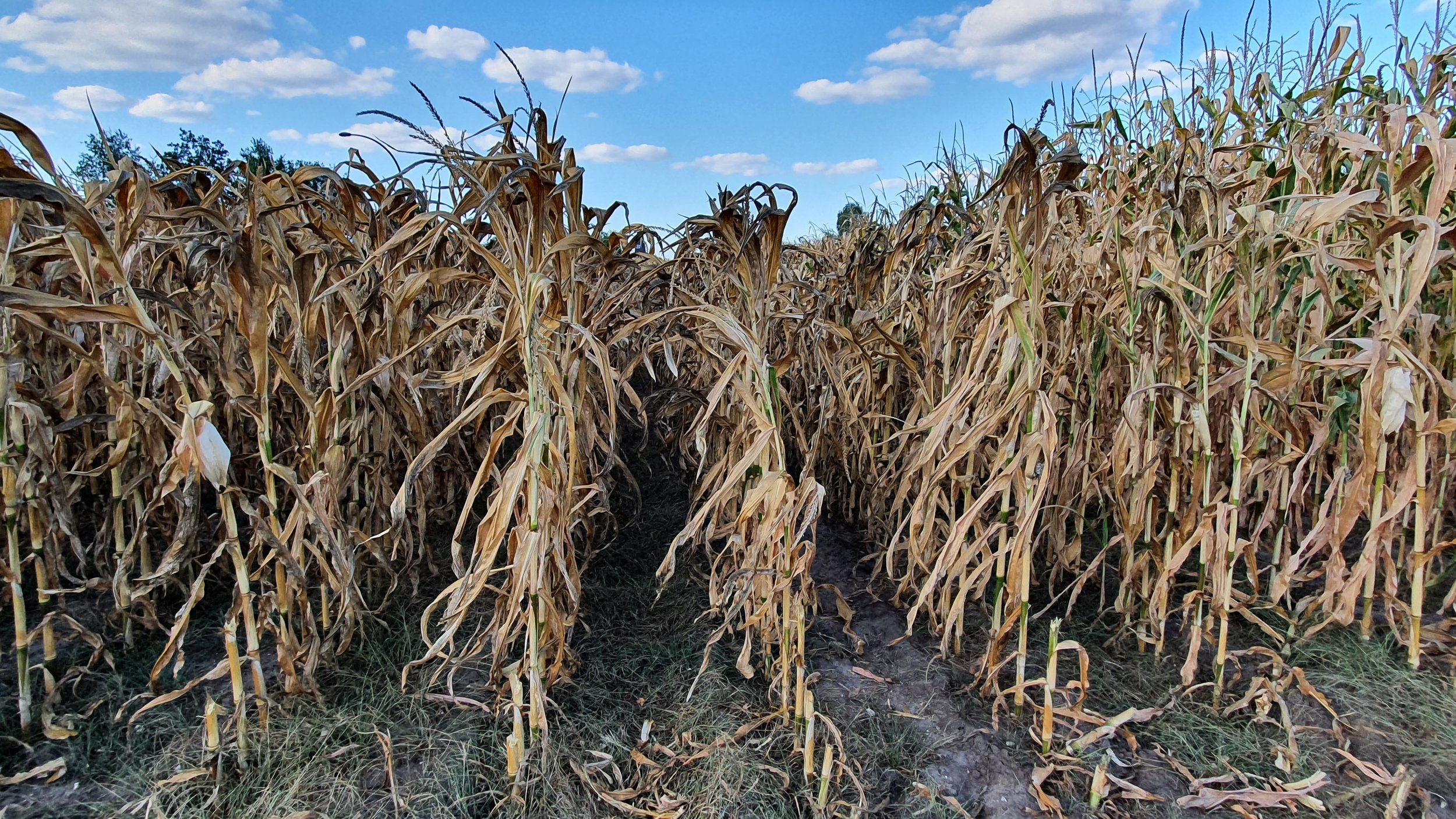
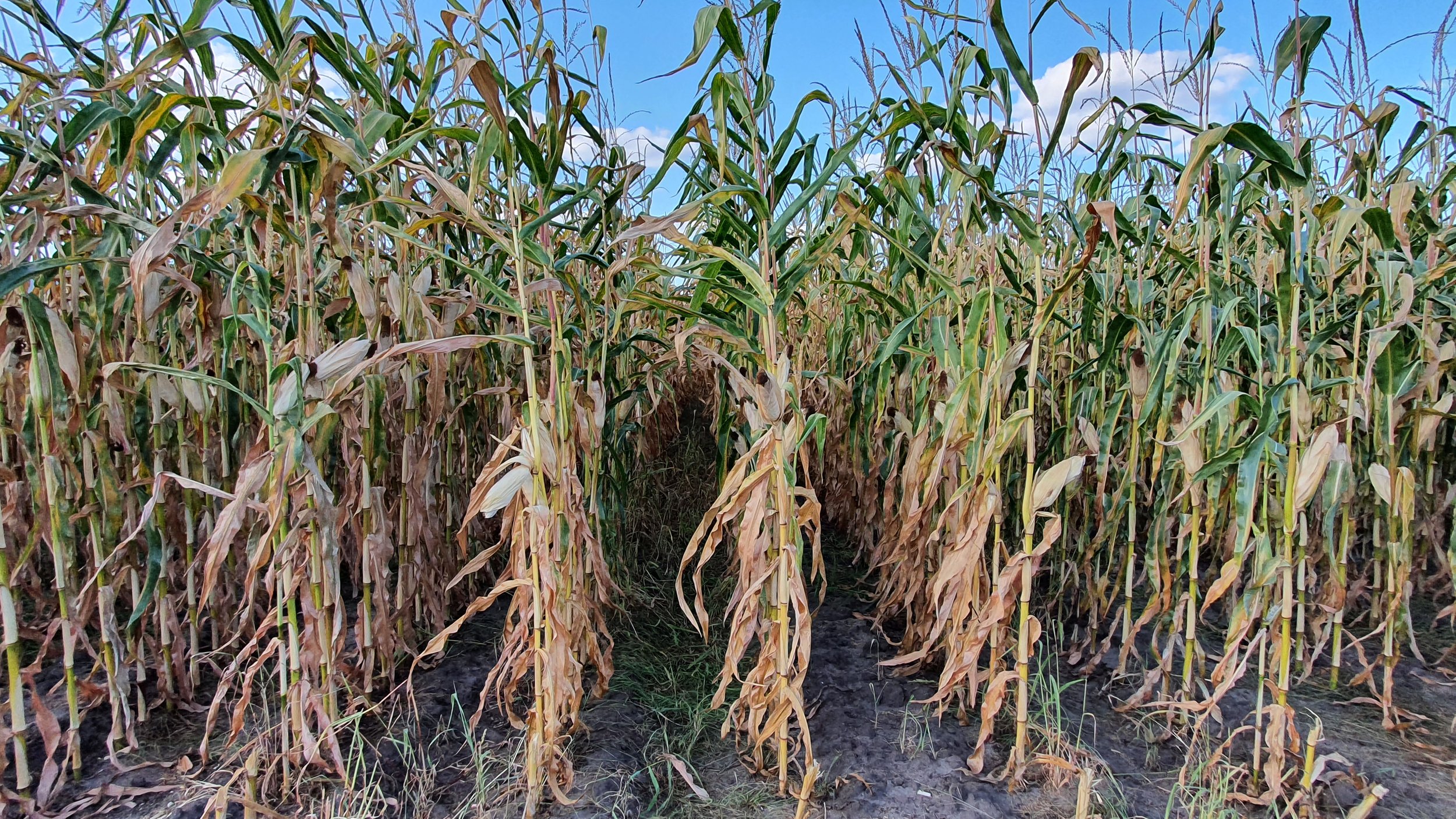
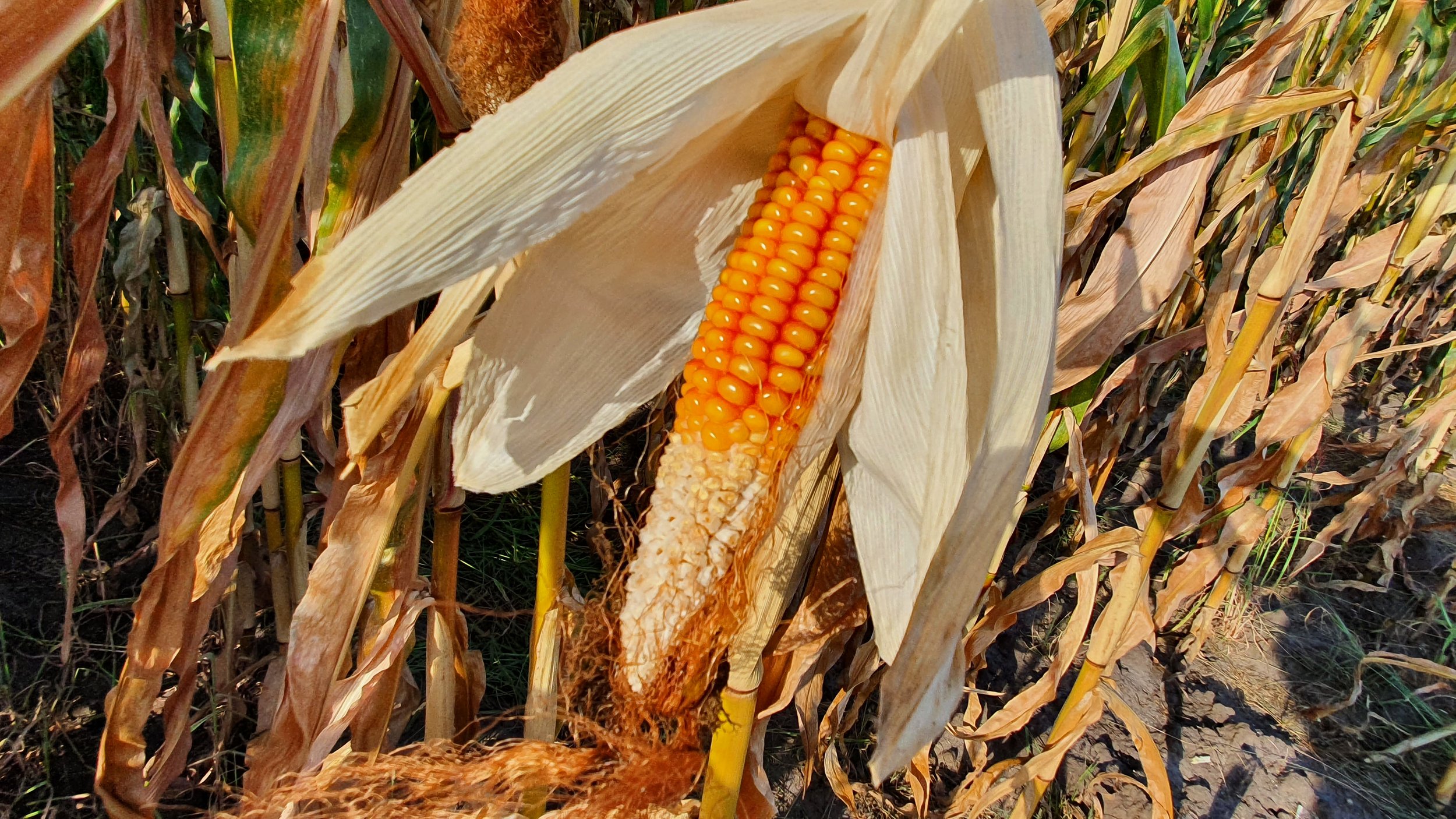
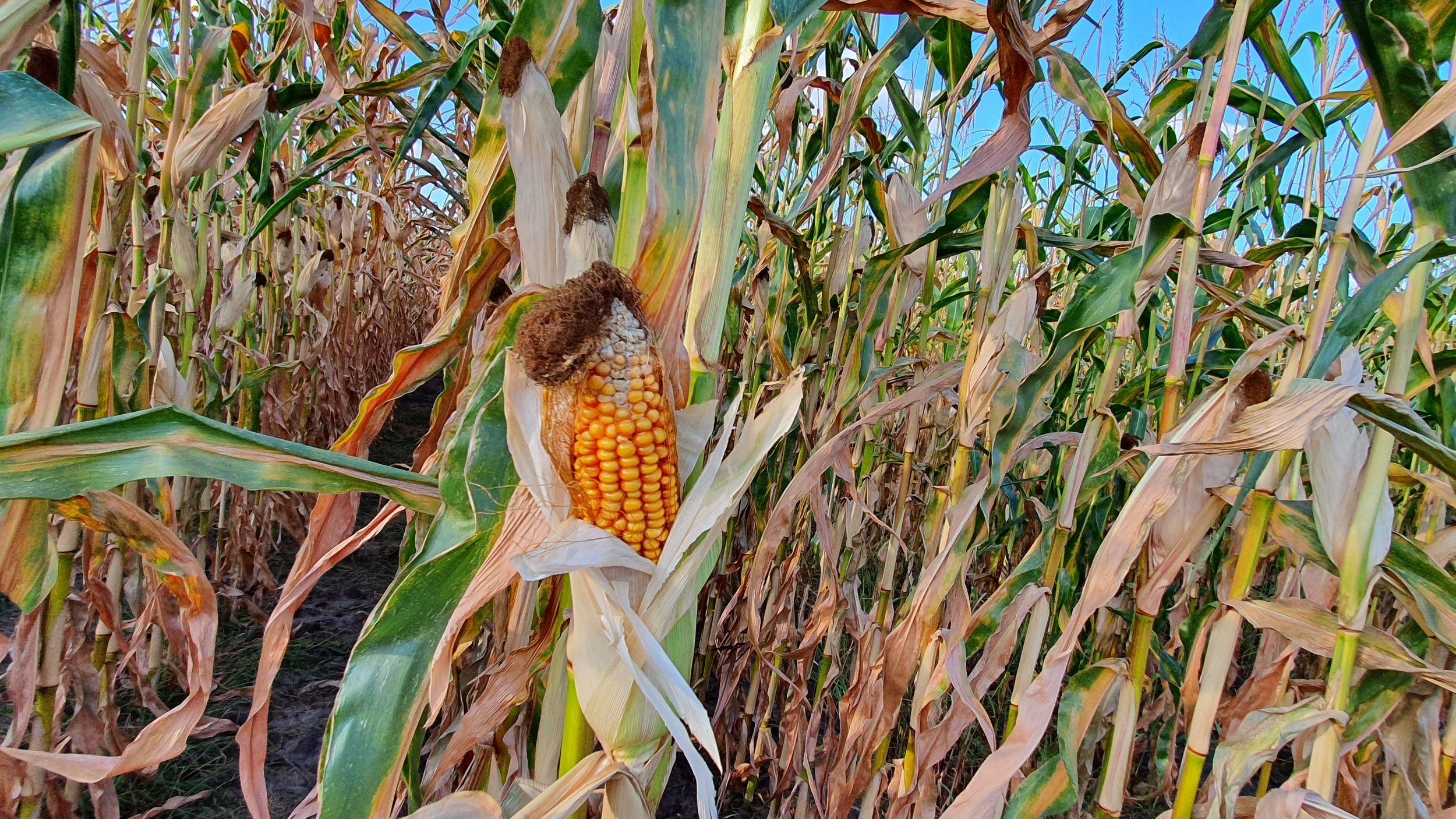
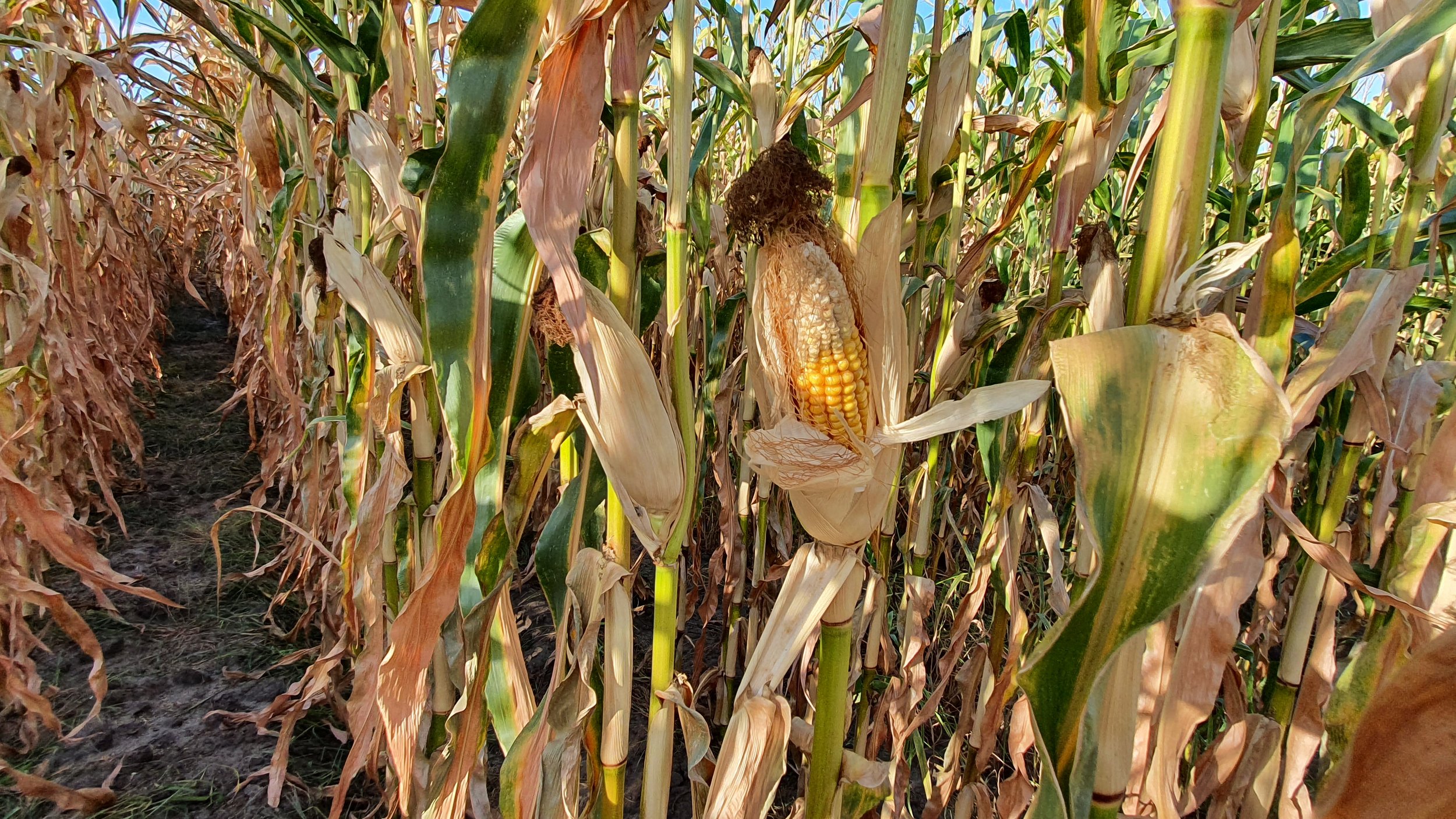
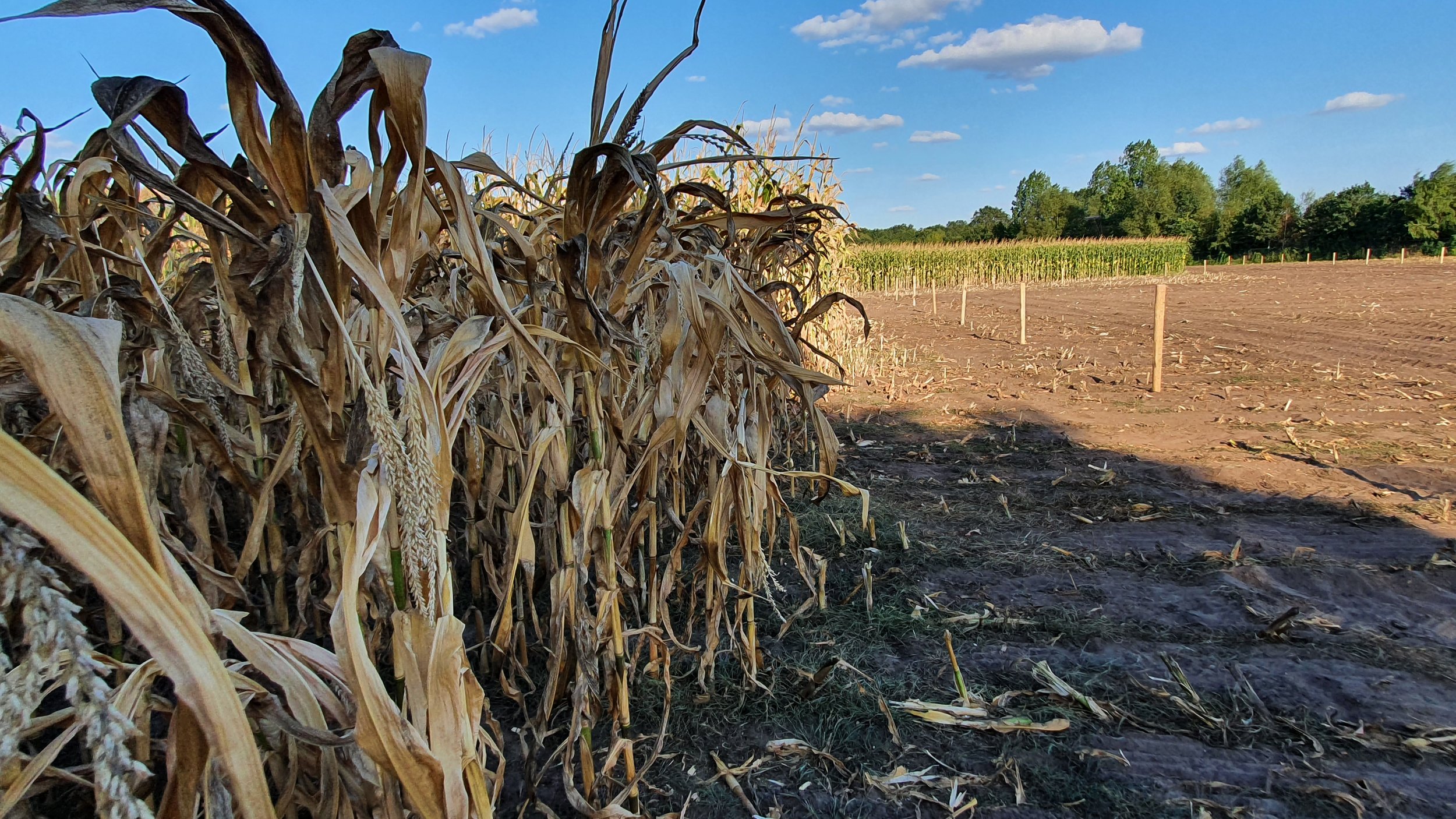
The gallery below shows the corn fields with stalks, dead leaves, and small, deformed, and undernourished ears on drought-stressed corn on August 27, 2022, in the Rekken research area and August 31, 2022, in the Hengelo study area. Still to measure the nitrate levels?
For the effect of drought on the corn stalks and the accumulation of nitrates that can end up being toxic see:
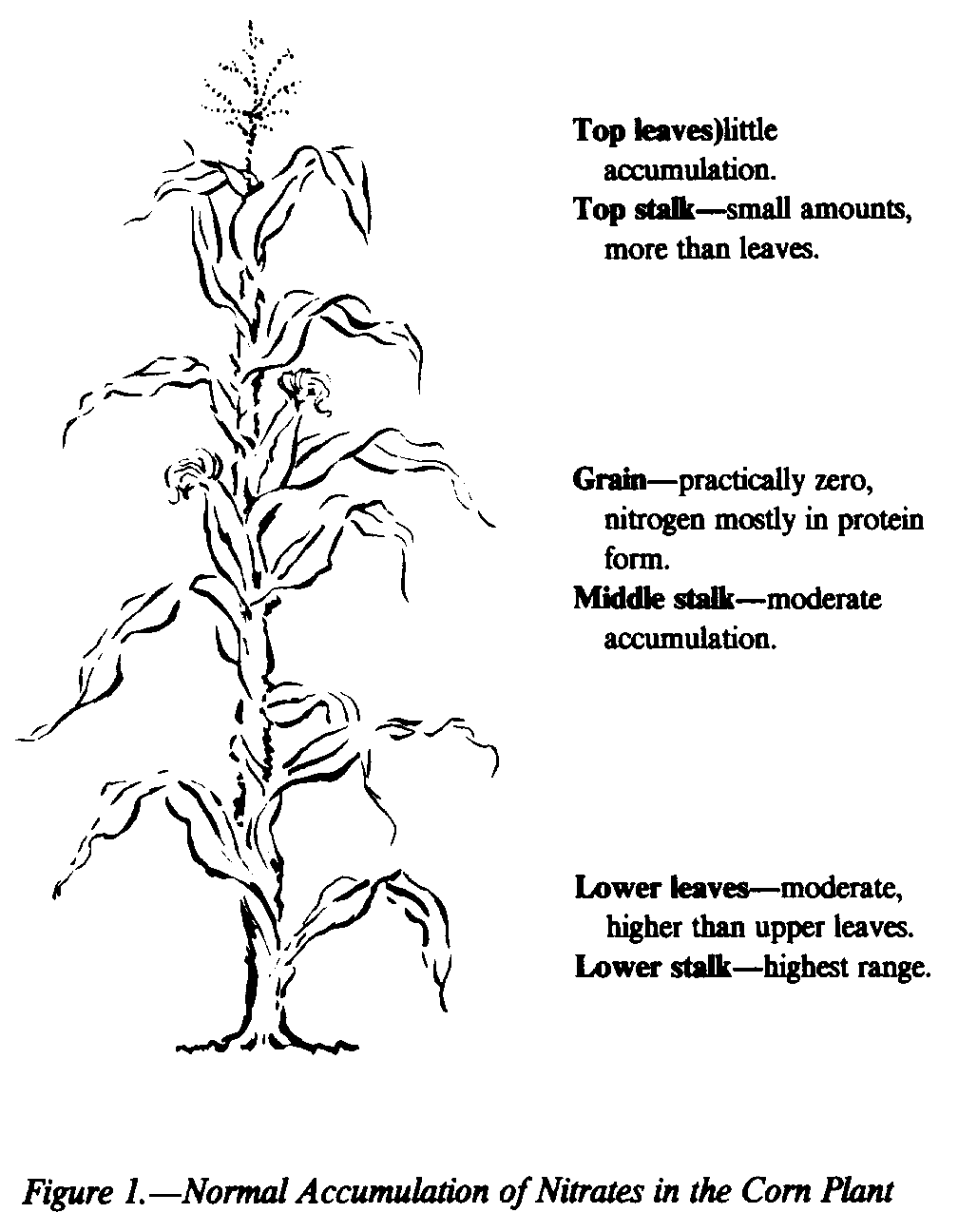
From UK College of Agriculture. USING DROUGHT-STRESSED CORN: HARVESTING, STORAGE, FEEDING, PRICING AND MARKETING
END OF SEASON CORNSTALK NITRATE TEST
Corn stalk cutter designed to sample from 6-14 inches above the soil level. Photo: Eric Anderson, Michigan State University (MSU) Extension.
For testing the stalk nitrate-N levels in corn plants, a protocol was outlined, according to the MSU Extension tip sheet.
Uniformly cut 8-inch stalk samples at 6 inches from the soil level. Samples were taken from fields with varying production management systems and growing conditions. Four consecutive stalks in a row where no planting spatial variability was observed were sampled at four locations in each field for a total of 16 samples per field. Then, stalk samples were sent to the Soil and Plant Nutrient Laboratory for analysis.
References
Nederlandse referentie: http://vruchtbarekringloopachterhoek.nl/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/App-voor-meten-nitraatgehaltes.pdf.
Factsheet Nitraat (Human risks).